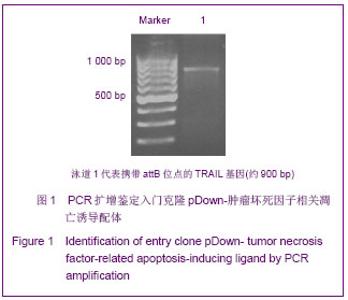
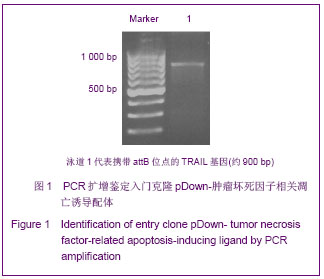
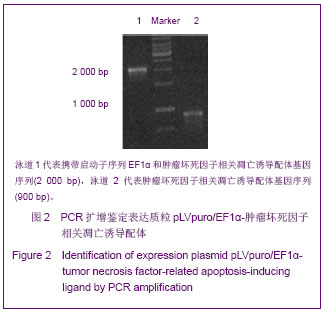
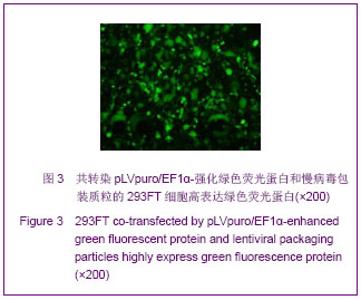
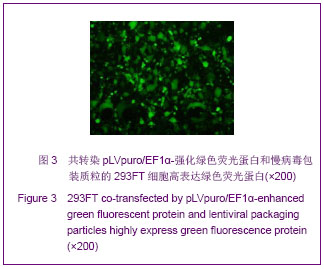
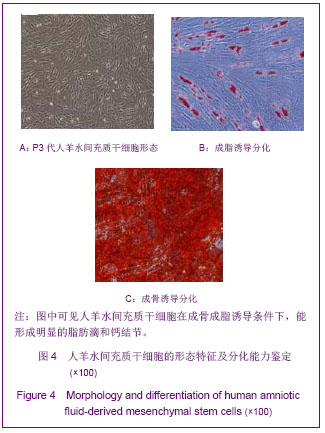
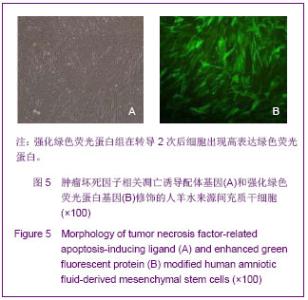
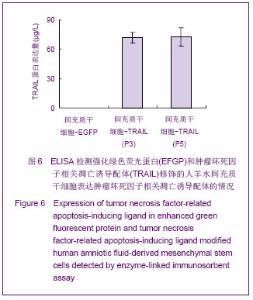
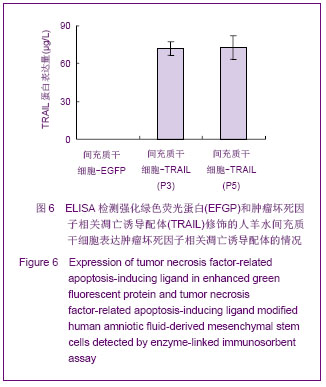
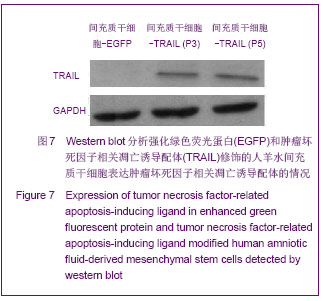
| [1]Cotrim AP, Baum BJ. Gene therapy: some history, applications, problems, and prospects. Toxicol Pathol. 2008; 36(1):97-103.[2]Chen YS, Li HR, Miao Y, et al. Local injection of lentivirus-delivered livinshRNA suppresses lung adenocarcinoma growth by inducing a G0/G1 phase cell cycle arrest. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2012;5(8):796-805.[3]Rossmiller B, Mao H, Lewin AS. Gene therapy in animal models of autosomal dominant retinitis pigmentosa. Mol Vis. 2012;18:2479-2496.[4]Dewey RA, Morrissey G, Cowsill CM, et al. Chronic brain inflammation and persistent herpes simplex virus 1 thymidine kinase expression in survivors of syngeneic glioma treated by adenovirus-mediated gene therapy: implications for clinical trials. Nat Med. 1999;5(11):1256-1263. [5]Raper SE, Chirmule N, Lee FS, et al. Fatal systemic inflammatory response syndrome in a ornithine transcarbamylase deficient patient following adenoviral gene transfer. Mol Genet Metab. 2003;80(1-2):148-158.[6]Lin CS, Ning H, Lin G, et al. Is CD34 truly a negative marker for mesenchymal stromal cells? Cytotherapy. 2012;14(10): 1159-1163.[7]Lee RH, Kim B, Choi I, et al. Characterization and expression of mesenchymal stem cells from human bone marrow and adipose tissue. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2004;14(4-6):311-324.[8]Chamberlain G, Fox J, Ashton B, et al. Concise review: meshenchymal stem cells: their phenotype, differentiation capacity, immunological features, and potential for homing. Stem Cells. 2007;25(11):2739-2749.[9]Bartholomew A, Sturgeon C, Siatskas M, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells suppress lymphocyte proliferation in vitro and prolong skin graft survival in vivo. Exp Hematol. 2002;30(1): 42-48.[10]Khakoo AY, Pati S, Anderson SA, et al. Human mesenchymal stem cells exert potent antitumorigenic effects in a model of Kaposi's sarcoma. J Exp Med. 2006;203(5):1235-1247.[11]Kidd S, Spaeth E, Dembinski JL, et al. Direct evidence of mesenchymal stem cell tropism for tumor and wounding microenvironments using in vivo bioluminescent imaging. Stem Cells. 2009;27(10):2614-2623.[12]Gao Y, Yao A, Zhang W, et al. Human mesenchymal stem cells overexpressing pigment epithelium-derived factor inhibit hepatocellular carcinoma in nude mice. Oncogene. 2010; 29(19):2784-2794.[13]Kucerova L, Altanerova V, Matuskova M, et al. Adipose tissue-derived human mesenchymal stem cells mediated prodrug cancer gene therapy. Cancer Res. 2007;67(13): 6304-6313.[14]Seo SH, Kim KS, Park SH, et al. The effects of mesenchymal stem cells injected via different routes on modified IL-12-mediated antitumor activity. Gene Ther. 2011;18(5): 488-495.[15]Ling X, Marini F, Konopleva M, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells overexpressing IFN-βinhibit breast cancer growth and metastases through Stat3 signaling in a syngeneic tumor model. Cancer Microenviron. 2010;3(1):83-95.[16]Los M, Panigrahi S, Rashedi I, et al. Apoptin, a tumor-selective killer. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2009;1793(8): 1335-1342.[17]Li X, Liu Y, Wen Z, et al. Potent anti-tumor effects of a dual specific oncolytic adenovirus expressing apoptin in vitro and in vitro. Mol Cancer. 2010;9:10.[18]Duiker EW, Mom CH, de Jong S, et al. The clinical trail of TRAIL. Eur J Cancer. 2006;42(14):2233-2240.[19]Ashkenazi A, Pai RC, Fong S, et al. Safety and antitumor activity of recombinant soluble Apo2 ligand. J Clin Invest. 1999;104(2):155-162.[20]State Council of the People's Republic of China. Administrative Regulations on Medical Institution. 1994-09-01.[21]Li YT, Chen SY, Wang CR, et al. Brief report: amelioration of collagen-induced arthritis in mice by lentivirus-mediated silencing of microRNA-223. Arthritis Rheum. 2012;64(10): 3240-3245.[22]Luche RM, Enssle J, Kiem HP. Abrogated cryptic activation of lentiviral transfer vectors. Sci Rep. 2012;2:438.[23]Kafri T, van Praag H, Gage FH, et al. Lentiviral vectors: regulated gene expression. Mol Ther. 2000;1(6):516-521.[24]Gallay P, Hope T, Chin D, et al. HIV-1 infection of nondividing cells through the recognition of integrase by the importin/karyopherinpathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1997; 94(18):9825-9830.[25]Ueda S, Yoshikawa M, Ouji Y, et al. Cynomolgus monkey embryonic stem cell lines express green fluorescent protein. J Biosci Bioeng. 2006;102(1):14-20. |